
What is FPGA?
FPGA (field-programmable gate array ) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturing – hence "field-programmable". The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL).
FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects that allow the blocks to be "wired together", like many logic gates that can be inter-wired in different configurations. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or merely simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory.
![)6J{ZA1DGE]TZC94Y0TF3$K.png](https://jpfile1.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/allpcb/web/image/20190605/6369532283384608837230145.png)
What is ASIC?
ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit) is a kind of integrated circuit that is specially built for a specific application or purpose. Compared to a programmable logic device or a standard logic integrated circuit, an ASIC can improve speed because it is specifically designed to do one thing and it does this one thing well. It can also be made smaller and use less electricity. The disadvantage of this circuit is that it can be more expensive to design and manufacture, particularly if only a few units are needed.
An ASIC can be found in almost any electronic device and its uses can range from custom rendering of images to sound conversion. Because ASICs are all custom-made and thus only available to the company that designed them, they are considered to be proprietary technology.
What is the Difference Between FPGA and ASIC?
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) and Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) provide different values to designers, and they must be carefully evaluated before choosing any one over the other. Information abounds that compares the two technologies. While FPGAs used to be selected for lower speed/complexity/volume designs in the past, today’s FPGAs easily push the 500MHz performance barrier. With unprecedented logic density increases and a host of other features, such as embedded processors, DSP blocks, clocking, and high-speed serial at ever lower price points, FPGAs are a compelling proposition for almost any type of design.
FPGA vs. ASIC Design Advantages

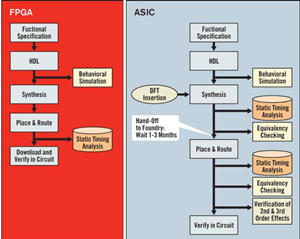
FPGA vs. ASIC Design Flow
The FPGA design flow eliminates the complex and time-consuming floorplanning, place and route, timing analysis, and mask / re-spin stages of the project since the design logic is already synthesized to be placed onto an already verified, characterized FPGA device.

 My Message
My Message
 Suggestions
Suggestions









Charles
2/13/2017 10:35:02 AM
Thanks for marvelous posting.